Where does cancer really come from?
In Part 2 I concluded with several questions:
-
If the trophoblast is indeed cancer that means that every pregnant woman has cancer, so how does the body get rid of the malignancy?
-
The trophoblast is a result of fertilization of an egg from donated sperm from the male species but cancer can ignite in both male and female without fertilization, how can that be?
- How does cancer occur and where does it stem from?
All will be revealed, but first, lets us honor one of the greatest men that ever lived, a brilliant embryologist Dr. John Beard (1857-1924) using almost primitive tools compared to today’s technology, unearthed the greatest enigma in medical history the origin of cancer.
Working as a Lecturer of comparative embryology at Edinburgh University he painstakingly studied various types of fish embryology and mammalian species including man. By chance he discovered what should have changed the course of medicine, the origins of cancer and how the body deals with it. It was Beards remarkable research that allowed him to conclude that Cancer was trophoblastic in origin.
 As I explained in Part 2, the trophoblast is the first biological structure (a differentiated cell) to develop from a Zygote (a eukaryotic cell that is formed by the fertilization of 2 haploid cells (male and female that contain unmatched chromosomes called Gametes)).
As I explained in Part 2, the trophoblast is the first biological structure (a differentiated cell) to develop from a Zygote (a eukaryotic cell that is formed by the fertilization of 2 haploid cells (male and female that contain unmatched chromosomes called Gametes)).
After fertilization, and within 3 days, a ball of 16 cells has developed referred to as a ‘Morula’, and by the 4th day the ball contains 58 cells referred to as a Blastocyst.
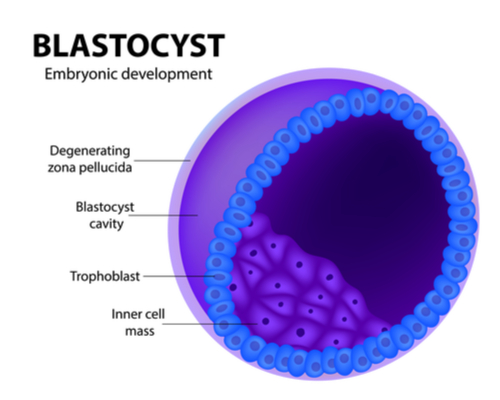
The Blastocyst, with its outer cellular structure consisting of trophoblast cells prepares to undertake the implantation process, within 5-6 days it starts prolifically, and without restraint, invading the uterine outer wall.
Both the uterus and the trophoblast perform a biological signaling dialog to complete the implantation within 11-12 days after fertilization.
Within 3 weeks the inner cavity of the blastocyst splits into 2 parts, the ‘Epiblast’ (which forms the initial embryonic building blocks by splitting into 3 parts producing the ‘ectoderm’,’mesoderm’ and ‘endoderm’) and the ‘Hypoblast’ (from which the yolk sac develops).
The Ectoderm (outer layer) will eventually give rise to Epidermis skin cells, brain neurons and pigment cells. The Mesoderm (middle layer) is the initial structure that will form the cardiac muscle, skeletal muscle cells,kidney, red blood cells and the smooth muscle in the gut. The Endoderm (internal layer) will form the lung cells, the thyroid and the pancreatic cells.

We also mentioned in part 2 a very important hormone that is secreted during early embryonic development ‘hCG’ Human Chorionic Gonadotropin, a glycoprotein that allopathic physicians look for in the bloodstreams of women to identify and confirm pregnancy (as identified by Ascheim and Zondek in 1928), but, as we have established is also a biomarker for cancer, so if detected in the bloodstream, outside of a pregnant state, then its presence would most likely confirm that cancer is present (as confirmed by Acevedo and Krichevsky in 1992) .
As Acevedo notes in his article hCG share common genetic and biochemical pathways for both human reproduction and malignant transformation.
In his article we are made aware that even plants can contract a type of cancer known as ‘crown gall disease’ caused by a DNA transfer from a Bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens.
Does Every Pregnant Woman have Cancer?

If the trophoblast is indeed cancer that means that every pregnant woman has cancer, so how does the body get rid of the malignancy?
The answer is yes, every pregnancy involves the growth of a malignancy in terms of the Trophoblast. A clue to this astonishing fact is two signaling growth factors i.e
- Transforming growth factor alpha/beta ( a polypeptide -string of amino acids that is upregulated in human cancer and induces oncogenic transformation
- Colony Stimulating factor I (Glycoprotein used for intracellular signaling pathway for cell proliferation and differentiation)
First of all, let’s understand some basic molecular biology:
Transcription is the process that makes a ‘xerox’ copy of the DNA template or gene blueprint into RNA which codes a protein.
A transcription factor (TF) is another protein referred to as an Activator protein that binds to pieces of DNA called Enhancers that bend the DNA nearer to the Gene Promoter (the protein that initiates transcription) to basically ensure that the correct genes are expressed in the correct cells of the body at the right time.
They recruit an enzyme called RNA Polymerase which actually performs the transcription of DNA to RNA.
ypical transcription factors are tumor suppression genes like P21 and P53 (The Master) regulating cell growth and apoptosis.

Generally, transcription factors allow cells to perform molecular logic operations combining different sources of information on what to read and copy from the gene blueprint, and to do this there maybe multiple TFs involved, even in an antagonistic relationship.
There are some 15 families of transcription factors, the one that we are concerned with is the basic Helix-loop-helix (bHLH) so named because of its 2 helices connected by a loop, one containing basic amino acids to facilitate the binding of the DNA, the other is the ‘GPS’ to identify the binding regions of the DNA.
- Hxt is a regulatory TF that activates very earlier in embryogenesis a series of events that transform the initial blastocyst into the trophoblast
- OCT-4 is involved in the self-renewal of undifferentiated cells and is used as marker as such. It regulates pluripotent or stem cell production and it is possible it has a role in the production of adult stem cells in the Yolk sac.
- Mash-2 controls the rapid cell division and promotes the invasive and migratory pattern of the trophoblast signaling DNA to begin replicating.
- Hand-1 comes into play when the early trophoblast has morphed into a Syncytiotrophoblast of Trophoblast ‘giant’ cells (so named because they undergo multiple cycles of endoreduplication amassing 1000 copies of DNA). This TF acts as a ‘brake’ by slowing down the trophoblast replication transforming into quiescent, non aggressive giant cells (referred to as Cellular Senescence) in concert with the P21 Tumor suppression gene.
In a cancer cell these TFs also play a role where Hxt and Mash-2 are ‘hard’ on activating DNA replication while OCT-4 and Hand-1 are suppressed (a scenario suggesting ‘all gas pedal and no brake’).
A special protein called ‘Cyclins’ are used to control cell progression using Cyclin-dependent Kinase (Cdk) enzymes. These proteins are necessary for cell division, but high levels of Cyclin found in cancer cells indicate an aggressive cancer, and would also indicate poor prognosis and lymph node metastasis in gastric cancers.
However in ovarian cancer the high levels of cyclin B generally indicates a less likelihood of malignancy but an aggressive kind is present if the levels are low.
It has also been observed that high levels of cyclin B in the cells deactivates P53 Tumor suppression.
 P53 Tumor Suppression
P53 Tumor Suppression
P53 is the body’s master tumor suppressor gene that is selenium based. P53 is a master lock that requires a key.
This key is UB7 gene that relies on Cesium to function. P53 requires Yttrium to function. Cesium supports the immune system and destroys cancer cells by raising the temperature where they simply self destruct.
The greatest concentration of Cesium and Selenium is in brazil nuts so you must eat at least 6 brazil nuts/day to keep the UB7 key functioning for p53.
The greatest concentration of Yttrium in food is Pignut Hickory (Who eats that…lol), or secondly Cabbage which you should eat regularly to maintain the functioning of the P53 Master lock, among many other great health benefits.
How Does the Body get rid of the Malignancy?
 During the life and work of Dr Beard in 1900 he was intrigued with how the body transforms the malignant characteristics of the Trophoblast a Benign mass of cells.
During the life and work of Dr Beard in 1900 he was intrigued with how the body transforms the malignant characteristics of the Trophoblast a Benign mass of cells.
If this one part of the puzzle could be solved, he would have the answer to reversing cancer.
As Dr Gonzalez remarks in his book the work of C.Ferretti, L.Bruni in their study ‘Molecular circuits shared by placental and cancer cells, and their implications in the proliferative, invasive and migratory capacities of trophoblasts’ 2007.
Also the work of Drs Murray and Lessey in their study ‘Embryo implantation and tumor metastasis: common pathways of invasion and angiogenesis’, both failed to ask the important question:
How does the body make the transition between the obvious malignant properties of the trophoblast to a benign structure later on ( In fact on day 56 ) in mammalian pregnancy?
Dr Beard studied other species in his career including fish, and in all embryonic stages of every mammalian species the same trophoblast transformation occurred.
Then he noticed that at the same time the trophoblast made this transformation, the pancreas was active secreting its enzyme granules and he concluded that it was the pancreatic enzymes that played a part in controlling placenta growth, preventing it from further invasion and cell replication.
Since the pancreas at this time contained digestive enzymes Trypsin and Amylopsin( in modern times known as Amlylase) he decided in 1905 to test his theory and injected trypsin in a mouse (Jensens mouse tumor model).
He reported in the British Medical Journal January 20, 1906 that results were heralded as a success.
Beard indicated that this degeneration of an asexual structure whether it be a cancerous tumor or trophoblast subjected to (Tryptic) digestion,
“I have observed many times and these experiments were not necessary to convince me that trypsin would have this effect and degenerate the tumor in the mice the same way it does within the trophoblast under normal development.”
 Parthenogenesis and Cancer
Parthenogenesis and Cancer

The second question:
-
The trophoblast is a result of fertilization of an egg from donated sperm from the male species but cancer can ignite in both male and female without fertilization, how can that be?
This phenomena is known as ‘Parthenogenesis‘ which is natural form of asexual reproduction where embryos can develop without fertilization.
This of course is common in plants that have both male and female reproduction capabilities since plants pollinate each other, either from wind driven pollen or carried by insects.
Parthenogenesis means ‘a virgin birth‘ and is known to occur in about 2000 species (but there could be more) in some unique fish, amphibians and lizards.
An example of Parthenogenesis is the Aphid species where at the start of the season only females are present whose reproduction is both parthenogenetic and viviparous (giving birth to live young).
This activity is repeated many times throughout the summer, producing many generations that survive between 20-40 days.
In the Autumn oviparous (egg production) occur where both males and females are produced.
This change from all females to a mixture of both male and females is speculated to be caused by either shorter days of light, temperature or food quantity/quality.
Then mating transpires, producing eggs that are hatched outside of the mother.
The eggs survive the winter and hatch in spring. the alternation of generations, especially between sexual and parthenogenetic generations
This heterogamy ( the alternation of generations, especially between sexual and parthenogenetic generations) occurs in bee and ant colonies where the queen reproduces many drones (male workers) parthenogenetically, but if the eggs are fertilised they become females which occurs when nature decides to replace the queen.
This science is quite involved especially ‘Thelytoky‘ ( type of parthenogenesis in which females are produced from unfertilized eggs, as for example in aphids, thēlys “female” and tokos “birth”) where some species have no males.
Furthermore, it is a fact that in the tropics there are virtually no parthenogenetic species, since the climate is conducive to a higher biological interaction (sex and sun are complimentary talking from a mammalian point of view of course).
Whereas parthenogenetic species are more common in Higher altitudes/latitudes, probably due to diminished biotic interaction, and the fact that mating takes up too much energy (which makes no sense since the pleasure must outweigh the energy dissipation but again talking from a mammalian perspective…lol).
This knowledge has brought us to a Historical Plateau because…
…in the Mammalian species parthenogenesis does not exist, but it does in the form of cancer since the trophoblast is cancer and cancer will always be trophoblast.
In the words of Dr Beard:
“Cancer is an ‘irresponsible trophoblast growing in the wrong place at the wrong time. Cancer is an aberrant (never to be fertilized) asexual parthenogenetic trophoblast that is devoid from nature’s complex, abortive, regulatory signaling”.

How does Cancer occur and where does it stem from?
Cancer is not genetic, unless you consider both chromosomal copies of the same gene as being faulty which is rare..5% rare.
This old failed medical theory that most aberrations of physiology and disease were genetic was suggested as a fact when microbiologists studying DNA were throwing away the regulatory proteins as ‘Junk’ DNA.
So, imagine for a moment, that for thousands of years the eukaryotic celled homo sapien species walked around carrying junk that he didn’t need.
Until 20 years ago or so somebody said, “maybe these proteins are doing something” and thus epigenetics was born.
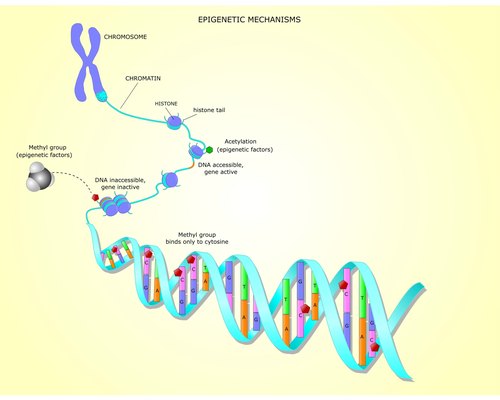
So we know that environmental signals influence our cells and react to the 150,000 receptors located on the memBRANE (Yes, this is the brain of the cell, not the nucleus ) of each cell.
We also know, that once the cell receives these environmental signals, some influence the nucleus where our DNA/Genes are stored.
So these signals activate DNA transcription, read the DNA copy (RNA) that influence our biology.
The whole gene can be read or a partial copy of the gene can be read.
Multiple transcription signals performing logical, chemically driven, decisions that include, which copy of the gene is read (on the father or mother chromosome depending on the environment that the father and mother were experiencing at the time just before conception), and how it is to be expressed, negatively (e.g cancerous expression) or positively.
Furthermore, if a gene is an oncogene (mutant gene) it may not necessarily be expressed at all.
So the idea that most diseases are caused by faulty genes is a flawed theory because 95% of cancer ignition is caused by environmental stimulus. For example:
Steve Mcqueen the actor developed metastatic mesothelioma (in the lining of the lungs) which is associated with asbestos exposure (since Mcqueen was an avid motorcycle racer he worked with asbestos, lining the exhaust pipes on the motorcycles.
Steve Jobs who developed a neuroendocrine tumor (islet cell carcinoma that affects the insulin producing cells of the pancreas) in his 20s due to exposure of lead used in soldering circuit boards.
In both of the above cases Toxicity provided the cancer ignition switch
Cancer overtime can also erupt due to the severe lack of nutrients the body needs, especially for cellular replacement (as I indicated before, Selenium is essential for DNA cell replication and a severe selenium deficiency any time during the 7 years it takes the body to replace all cells could potentially give rise to cancer).
Severe nutrient deficiency can also provide the cancer ignition switch
Despite what urologists think (or don’t know in some cases), prostate cancer can develop due to hormonal imbalance, specifically to an excess of estrogen versus testosterone which typically occurs in males as they age, so diet is the only preventative measure, ensuring that cruciferous vegetables (Cauliflower, Broccoli etc) are in the diet to inhibit too much estrogen production.
Hormonal imbalance can also provide the cancer ignition switch
This also applies to the enlargement of the prostate, because too little DHT (Dihydrotestosterone ) is being produced due to the estrogen/testosterone imbalance.
There are also example of cancer erupting in individuals due to years if excessive alcohol consumption, and it is my belief that this behaviour overwhelms the detox function of the liver and Toxicity provides the cancer ignition switch in conjuction with severe nutrient deficiency.
Where does cancer stem from?
Finally, the second half of the question:
How does cancer occur and where does it stem from?
The clue is in the question, from our stem cells.

There are 2 types of stem cell, embryonic and adult stem cells. The former are used in the initial stage of the trophoblast. You may recall that the trophoblast develops before the embryo from a single stem cell produced from the zygote.
If you ask some medical professional where adult stem cells come from, they don’t know.
Logically they can only derive from one place..the Yolk sac.
During the early stages of pregnancy, the adult stem cells make their incredible journey from the yolk sac via the umbilical cord to the growing fetus where, eventually they nest in most of our tissues, waiting to be used as replacement ‘spare parts’ as needed by the body during the human organism’s lifetime
(…I know what you’re thinking God has thought of everything) that is why the human body is self healing and self regulating once the body contains the right fuel.
If you have read this article you are now in the possession of certain facts that have escaped mainstream medicine and what was thought of as a biological impossibility.
In the final part I will inform you of the pioneers that made successful cancer treatment possible and have helped many people through their various health challenges, converting fear to hope, a situation that could occur if we all went down the road of functional medicine, but that’s another issue and maybe food for another article.

[The members of “The People’s Front of Judea” are sitting in the amphitheatre; Stan has just announced that he wants to be a woman and wants to be called “Loretta,” and is explaining why]
Stan: I want to have babies.
Reg: You want to have babies?!?!
Stan: It’s every man’s right to have babies if he wants them.
Reg: But … you can’t HAVE babies!
Stan: Don’t you oppress me!
Reg: I’m not oppressing you, Stan. You haven’t got a womb! Where’s the foetus gonna gestate? You gonna keep it in a box?
Quote from Monty Python’s Life of Brian 1979
Check out the previous articles in this series
https://www.extremehealthacademy.com/cancer-navigating-the-historical-road-to-truth-part-1
https://www.extremehealthacademy.com/cancer-navigating-the-historical-road-to-truth-part-2
References/Acknowledgments
- The Trophoblast and the origins of cancer ( 2009 book) Nicholas Gonzalez MD, Linda Isaacs MD.
- Ectoderm,Mesoderm,Endoderm Wikipedia
- hCG the hormone of life and death, a review Hernan Acevedo (May 2002 Journal of experimental therapeutics and oncology Vol 2 Issue 3)
- HxT encodes a basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor that regulates trophoblast cell development ( 2005) J.Cross, M.Flannery, M.Blanar, E.Steingrimsson, N.Jenkins, N.Copeland, W.Rutter, Z.Werb
- The HAND1 bHLH Transcription factor regulates Trophoblast differentiation via multiple mechanisms ( NCB1 2000 ) I.Scott,L.Cartwright,P.Riley,D.Redu,J.Cross
- Cyclin B/Parthenogenesis/Aphids/Heterogamy Wikipedia
- Parthenogenesis Marc Srour Bioteching Dec 2010
Author: Eric Malouin