Introduction
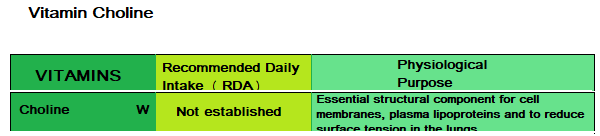
Choline is critical for sustaining life which is why it is a very essential nutrient.
Its various biological functions include the formation of our cell membranes using particular Phospholipids that are synthesized from Choline which are Phosphatidylcholine and Sphingomyelin.
Both these phospholipids are also used for cell signalling.
Choline is also used as a precursor for an extremely important Neurotransmitter Acetylcholine, and an assembly component for VLDL (Very low density Protein) a lipid raft transport for the liver.
A metabolite produced by the oxidation of Choline called Betaine is used as a methylation molecule for up to 60% of the methyl groups used for Homocysteine methylation.
Cell Membrane Integrity
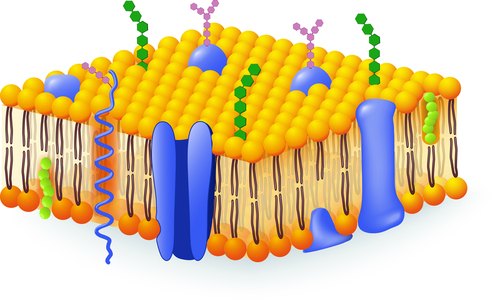
Cell Membrane Infrastructure is built from Phospholipids, that consist of a 2 layer Amphiphilic (meaning there are 2 Hydrophobic (waterproof) Fatty Acid Tails), and a Hydrophilic (selectively permeable) Head, held together by a Glycerol (as in Glycerin soap) substance.
In fact, the first Phospholipid was found in 1847 as a Lecithin, in this case, Phosphatidylcholine within Egg yolks.
Cell membranes need to be structured this way to allow nutrients to enter the cell and waste products and energy to exit the cell.
So the combination of being Hydrophobic provides a boundary between the contents of the cell and the Extracellular environment, and Hydrophilic to provide selective permeability allowing substances to move across the membrane to enter and exit the cell.
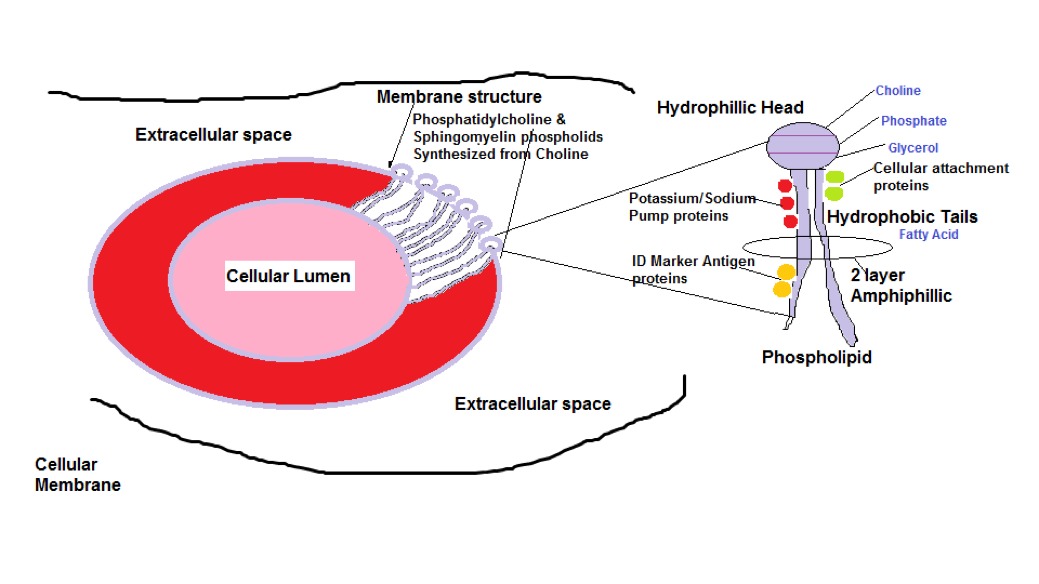
This arrangement is shown in diagram 1, depicting also, the various proteins that make up the Phospholipid structure namely the 30 million or so Potassium/Sodium pumps that exist on the cell that help transport the substances entering and exiting the cell.
The ID Marker Antigen proteins identify the cell to the immune system, and the Cellular attachment proteins which are receptor sites for Paracrine signaling (e.g Prostaglandins that were described in Part 3 of the series ‘Metabolic Typing’)
Diagram 1: Cellular Membrane Structure
Cell Signaling
Does anybody know how a telephone exchange works.
So you pick up the telephone and dial the number and then it rings at the telephone of the person you are calling.
But the system in between is a series of switch arrays, relays and multiplexers that are programmed to talk to other telephone exchanges to switch the call through..think of 2 cans connected together with a chord and multiply that by a billion…lol.
In the old days there were human switchboard operators sitting in front of a patch panel using physical jacks that plugged into the panel to connect callers to receivers through other exchanges.
So one call could activate many solid state switches and relays in order to complete the circuit.
The simplicity of functions involved two state switching either ‘On’ or ‘Off’ that can become more complex with ‘logic’ operands such as the basic ‘AND’, ‘OR’, EXCLUSIVE’, ‘INCLUSIVE’.
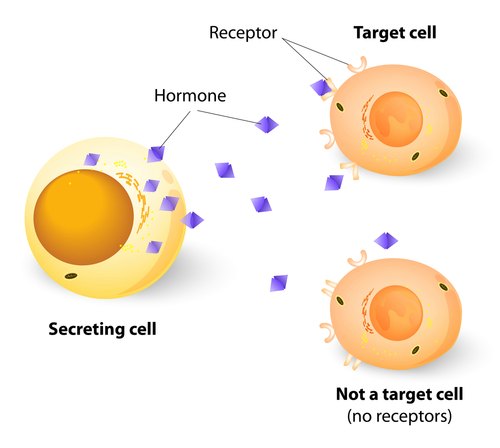
Cell signaling is based on the same principle, where a signaling molecule ( Ligand ) from one cell binds to a receptor on another cell to initiate a signal transmission (Paracrine signaling).
Once the signal is received by the cell receptor, this could trigger a series of signal transfers through other molecules within the same cell before a response is triggered.
Principally, it is a biological telephone exchange of sorts, achieved at the ‘Extracellular’ and Intracellular level.
But of course the mammalian chemical signaling was not designed on the Telephone PABX exchange, rather the other way round..lol.
The fancy name for molecule chains that relay signals inside the cell is Intracellular Signal Transduction Pathways.
The purpose of cellular signaling is to change the cells behavior or characteristics as in hormone signaling.
Relay signaling molecules can be Proteins, Ions or Phospholipids.
In biology the trick to alter protein activity, by switching it on or off, or enhancing its activity, is Phosphorylation (adding a Phosphate group to a Protein by using an enzyme called a ‘Kinase’).

Like a switch, Phosphorylation can be inactivated by Phosphatase enzymes (the off position).
Choline’s Phospholipids Phosphatidylcholine and Sphingomyelin act as precursors for intracellular message molecules (Secondary messengers) whose purpose is to change the characteristics of the cell to either Proliferate, Differentiate, Migrate or Die (Apoptosis).
These message molecules produced by the choline precursors are Diacylglycerol (DAG) and Ceramide respectively. We know that DAG, although part of the cell membrane, can activate a Protein Kinase (PKC) target, triggering a phosphorylation of its own target molecule, to activate a cellular response.
Other cellular signals produced by choline, involve immune system function Leukocytes namely Platelet Activating Factors.
Finally, we mentioned ‘logic’ above and indeed that is what occurs when pathways interact with other pathways, e.g 2 pathways may be required to trigger a response which would involve Pathway 1 ‘AND’ Pathway 2, alternatively either pathway can initiate a response so the logic operation would be Pathway 1 ‘OR’ Pathway 2.
Cell Signaling: Neurotransmitter Acetylcholine
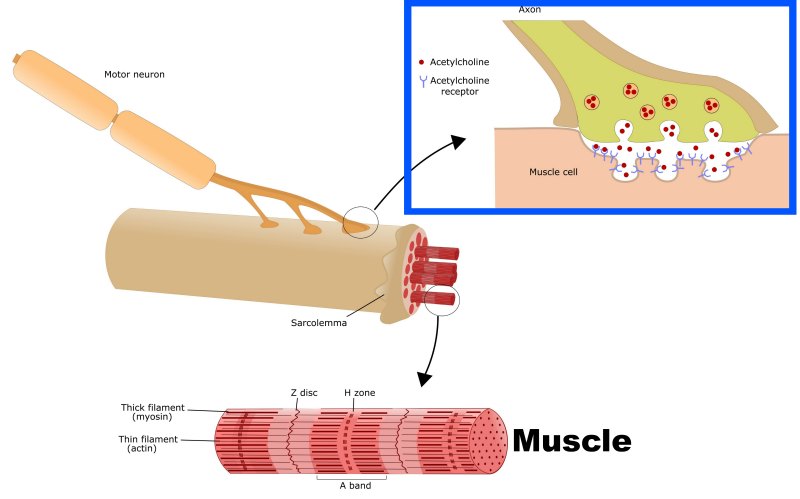
Neurotransmitter Acetylcholine is crucial for neuromuscular control, a chemical released to activate muscle movement.
It is also provides vital signaling within the Autonomic nervous system (ANS).
Curiously, it was 19th century France when Claude Bernard ( French physiologist 1813-1878) experimented with poisons like Curare a deadly plant poison used by South American Indians who used it to lace darts to paralyze their prey.
Bernard discovered that this poison blocks muscle ability to respond to stimulation.
A specialized area called the Neuromuscular Junction was the target for the poison.
Within the ANS this area is the Neuroeffector junction but this is not affected by the poison.
This junction within the ANS is where Acetylcholine works between the Autonomic nerves and the Smooth Muscle which again was discovered using a poison Muscarine contained in Mushrooms.
Acetylcholine is the final neurotransmitter for the Parasympathetic Branch of the ANS, while Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) is the neurotransmitter for the Sympathetic Branch (although I understand that the sympathetic side does use Acetylcholine for the salivary glands).
Within the Brain, Acetylcholine is also used for neurotransmission purposes affecting Cognitive functions that include Arousal, Attention, Memory and Motivation.
Pharmaceutical Targets

Drugs have been manufactured that alter Cholinergic transmission.
This class of drug are known as Anticholinergic which include Scopolamine for motion sickness, and other drugs, that are used to treat Gastrointestinal Disorders like Peptic Ulcers, Diverticulitis, Ulcerative Colitis, Cystitis, Prostatitis, Respiratory Disorders, Insomnia, and Vertigo.
This is complete insanity……for the sake of motion sickness, somebody would agree to taking a drug which effectively runs the risk of inhibiting autonomic nerve function the same way poisons like Sarin, Botulinum Toxin, Curare, and Muscarine do.
They say that ignorance is bliss, the majority of the population have never heard of Acetylcholine, let alone its vital function in the human body.
We also know from our discussions on the Microbiome that Diverticulitis, Ulcerative colitis are caused by Microbiome imbalance.
Furthermore, if Acetylcholine is the main neurotransmitter for the Parasympathetic branch of the ANS, and, that the Parasympathetic branch regulates our rest/sleep cycle, then why on earth would you prescribe an Anticholinergic drug that blocks this neurotransmitter, for insomnia…..do allopathic physicians actually attend medical college?
Dietary Sources of Choline

One of the richest sources of choline are eggs, one of nature’s wonderful foods.
I have included Table 1 showing all of the nutrients in eggs followed by Table 2 showing the total amount of Choline and Betaine in some common foods.
Some foods actually contain some amount of Choline’s metabolite Betaine.
Betaine is an amino acid created by its precursor Choline from an essential amino acid Glycine (one of the amino acids that produce Glutathione ( the body’s natural antioxidant ).
Table 1 Nutrition in an Egg

Consume the whole egg because if you discard the albumin (egg white) you will be robbing yourself of much needed Potassium and Sodium. Furthermore, there is nothing wrong in eating 4 eggs/day..you need the cholesterol..don’t ask your family doctor he will probably send you to a psychiatrist for a prescription of Prozac because he might think you are depressed..wanting to eat all those dangerous eggs..lol.
The RDA has been set for Choline which is an average of 475 mg/day, and Betaine between 50-100 mg/day.
Choline/Betaine as a Methylation Molecule
As mentioned earlier Choline’s metabolite Betaine is used as a methylation molecule for up to 60% of the methyl groups used for Homocysteine methylation.
As you may recall from previous articles Methylation is a key process for almost anything biochemically functioning in the body including DNA regulation and Integrity, Neurological health, Liver Detoxification, Kidney Filtration etc
Like metabolism, methylation degrades with age unless you supplement with essential nutrients. Folate (B9), Vitamin B6 and B12 should be at the top of the list, including Choline (providing methyl donors) since they are directly involved with methylation.
I have included the simplified methylation cycle again to reinforce how crucial these essential nutrients are.
Diagram 2: Methylation Cycle Simplified with Dietary Sources
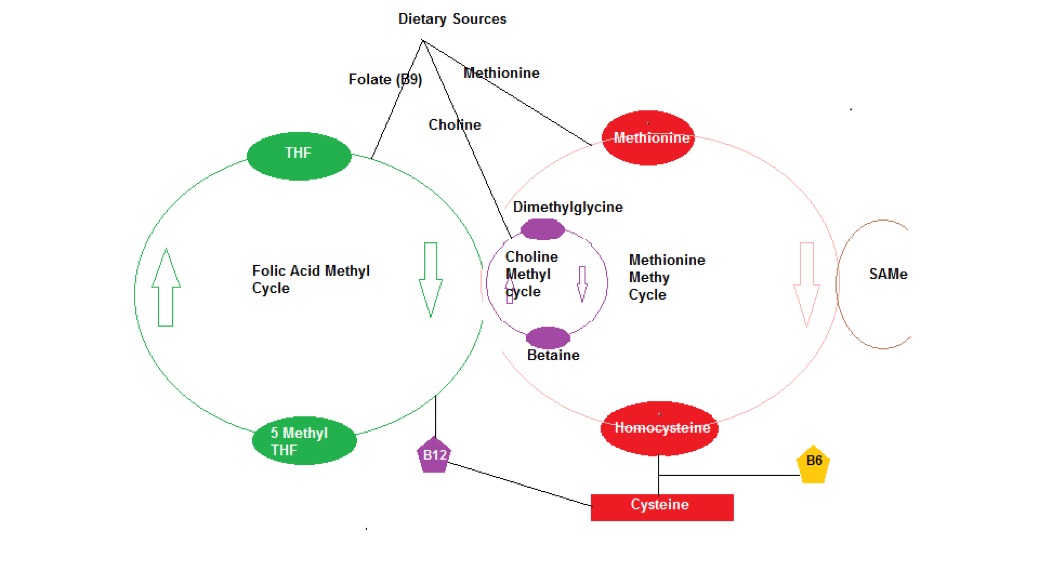
In the Methylation (Methionine) cycle shown in diagram 2, Methionine which comes from the diet (meat protein for example) is converted to the main Methylation Donor (SAMe) and within the cycle SAMe loses its methyl group and subsequently converted to Homocysteine.
Liver cells with the use of a catalyst Vitamin B6, Homocysteine is converted to the amino acid Cysteine which can then be used to form Glutathione or converted back to Methionine using Methyltetrahydrofolate (THF) in the Folic Acid Cycle assisted by Vitamin B12.
High plasma Homocysteine is sometimes an indication of Vitamin B complex deficiency either singly or a combination of B6,B12,and B9 (folic acid).
Methyl Donors
Humans who consume a balanced diet will ingest approximately 50 mmol (micromoles) of dietary Methyl groups/day ( = 15 mcg/day) including Folate, Methionine and Choline.
At least 60% derived from Choline’s metabolite Betaine.
The methylation pathways closely interconnect these dietary groups and Vitamins B6 and B12.
Pathway intersects occur at the Methionine/Homocysteine cycle.
Deficiency or low supply of one dietary substance will dictate what is used as a methyl group, so in the case of a low supply of choline or its metabolite betaine, the body will use methyl THF (Folate ) and vice versa. This arrangement is shown in Diagram 2.

“Man is the only creature that consumes without producing. He does not give milk, he does not lay eggs, he is too weak to pull the plough, he cannot run fast enough to catch rabbits. Yet he is lord of all the animals. He sets them to work, he gives back to them the bare minimum that will prevent them from starving, and the rest he keeps for himself.”
― George Orwell, Animal Farm
Check out the Previous Article in this series:
https://www.extremehealthacademy.com/90-essential-nutrients-part-1-overview/
https://www.extremehealthacademy.com/90-essential-nutrients-part-2-b-vitamins-1-6/
https://www.extremehealthacademy.com/90-essential-nutrients-part-3-b-vitamins-7-12/
https://www.extremehealthacademy.com/90-essential-nutrients-part-4-vitamins-acde/
https://www.extremehealthacademy.com/90-essential-nutrients-vitamin-d/
https://www.extremehealthacademy.com/essential-nutrients-vitamin-e/
https://www.extremehealthacademy.com/essential-nutrients-vitamin-k/
References/Acknowledgments:
- Phospholipids, Anticholinergic, Acetylcholine, Wikipedia
- Choline Oregon state University ( Linus Pauling Institute Macronutrient info centre
- Cell- -The plasma membrane Sciencejrank.org
- Egg whites vs egg yolks What do you use ? Grace Derocha 2011
- Choline The Worlds Healthiest foods Website
- Modern Nutrition in health and disease M.Shils, M.Shike, C.Ross, B.Cabellero,R.Cousins
- Diet, methyl donors & DNA methylation interaction between dietary folate,methionine and choline Niculescu, Zerisol NCBI 2002
- The second brain Book Michael Gershon MD
- Animal Farm Quote George Orwell
Author: Eric Malouin