Introduction
There is a plethora of information on the web concerning Vitamin K1 (Phylloquinone) including its bacterial produced ‘cousin’ K2 (Menaquinone).
In my articles on the microbiome I discuss bacterial manufactured vitamins like the B complex including K2, that sustains our biology in times of food shortage for example.
In a healthy gut it means that these vitamins should be bioavailable being absorbed within the bowel.
What most people are not aware of is the low absorption of that dietary K1 (from vegetables, fats and oils) which is barely 10% even if it is eaten raw or juiced the absorption rate is the same.
However with K2 dietary sources (Fermented foods like cheese, soy, vegetables) all of the K2 is absorbed..well this is a little surprising, but is it?
Given our biological design is, as always, way ahead of us, because this is why K2 has been made available to us by our life saving bacteria.
Another clue that substantiates low K1 versus K2 is, that deficiency has been observed when long term antibiotics are used, destroying our gut flora and its ability to produce VitK.
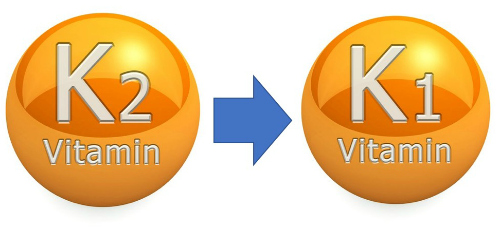
Interestingly both K1 and K2 provide more or less the same functions, and under certain circumstances the body has the ability to convert K1 to K2
Vitamin K – Biological function
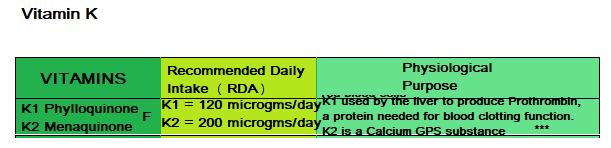
I believe most people are aware of Vitamin K1 which was always referred to as Vitamin K before the discovery of certain species of gut microbes that synthesized their form of Vitamin K which was called ViTK2. The three main biological functions of Vitamin K is:
- Blood Coagulation
- Support bone integrity.
- Prevention of soft tissue calcification and calcium distribution
Blood Coagulation
VitK is an essential component for normal blood plasma protein building.
When it is absorbed in the Epithelium, a Chylomicron LDL Particle is used to transport the absorbed Vitamin K to the liver.
All of Vitamin K1 is kept within the liver preserved tightly for the purposes of blood coagulation, but K2 when received by the liver is distributed via LDL transport to other tissues of the body.
The liver uses K1 to synthesize proteins that are required for blood coagulation and to control calcium binding in bone and tissue.
VitK is chemically 2-methyl-1,4-napththoquinone, a derivative of Methane & Naphthalene (Naphthalene is a substance that was discovered in 1820 when Coal tar (made of naptha, creosote and pitch) a substance used in soaps and ointments was distilled producing a white solid with a pungent odor..now I know where moth balls came from, that my mother used to protect her clothes from being eaten.
Interestingly it was Michael Faraday (the great British scientist who made phenomenal contributions to the study of electromagnetism and electrochemistry), who helped discover Naphthalene.
Vitamin K is an essential cofactor (Coenzyme) for a liver enzyme Gamma-glutamyl carboxylase formed by the combination of a carboxyl group (carboxylic acid made from amino acid & acetic acid) with Glutamic acid (GLU) one of the amino acids that produce Glutathione that was discussed in the article on Vitamin E to produce Carboxyglutamate (Gla) an acidic amino acid.
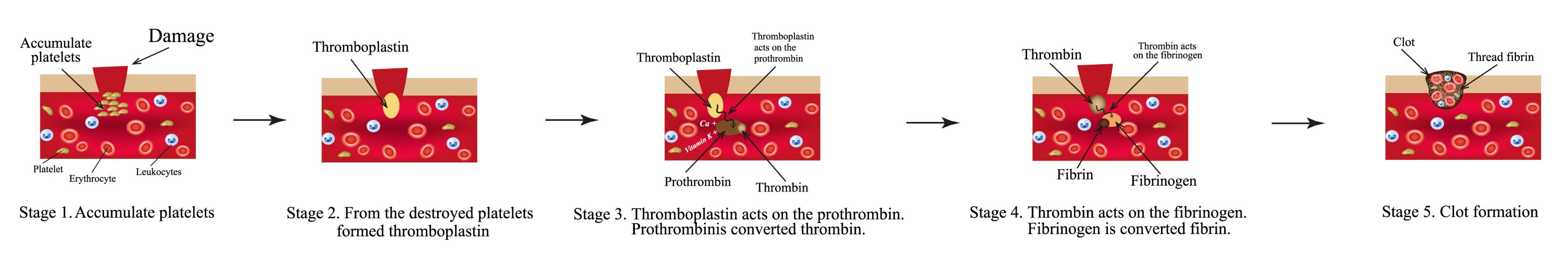
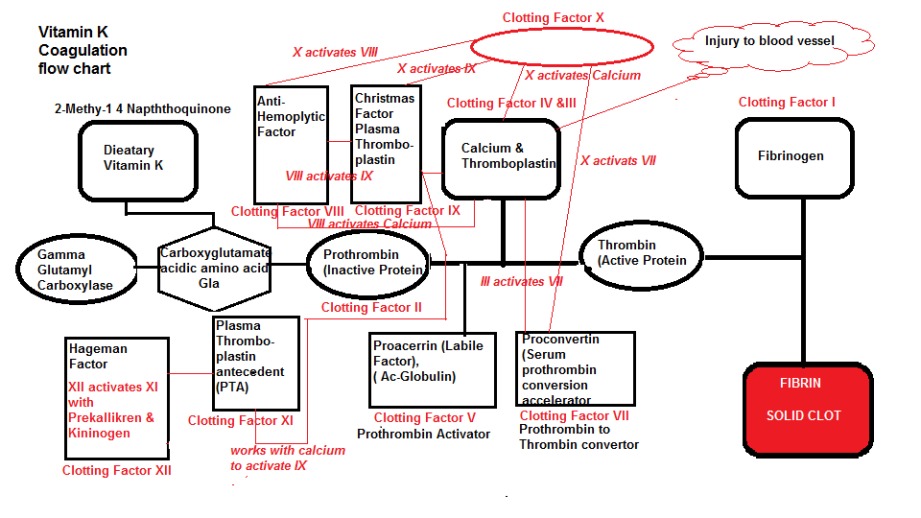
Twelve plasma clotting factors synthesized as inactive precursors (zymogens) in the liver, and proteins, essentially provide a conversion pathway for Prothrombin-Thrombin-Fibrinogen -Fibrin.
For such a simple process of changing blood viscosity to prevent bleeding to death is highly complex as shown in Diagram 1.
I don’t expect the reader to absorb this diagram but just to appreciate its complexity.
Basically all 12 clotting factors float around in the blood inactively, but when an injury occurs a rapid ‘Coagulation Cascade’ is triggered creating a multitude of activation.
This multi-step process is inactivated without the presence of Vitamin K.
Diagram 1: Coagulation Flow Chart
Support Bone Integrity
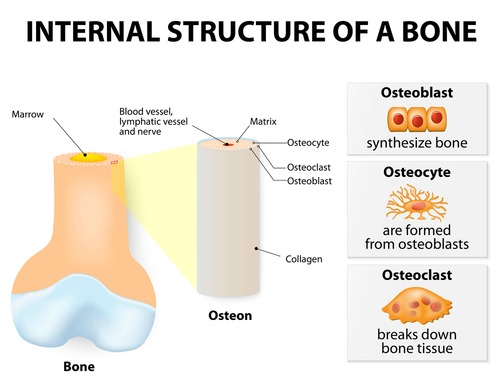
It was discovered after the Gla residue was found in plasma that this same protein was located in bone, which was named Osteocalcin, a Bone Gamma-Carboxyglutamic acid containing protein.
It was also found in Dentin (in teeth ), and since this protein had Gla domains, its synthesis is dependent on ViTK.
Osteocalcin is secreted only by Osteoblasts the cells that rebuild bone (Osteoclasts are cells that dissolve or break down bone which is how the body renews the body’s structure using a combination of Osteoclasts and Osteoblasts).
From our previous discussion concerning Vitamin D, we now know that its primary importance is to maintain serum calcium and phosphorous for bone ossification. Therefore it is important that VitD and VitK are both present to ensure bone integrity.
Prevention of Soft Tissue Calcification
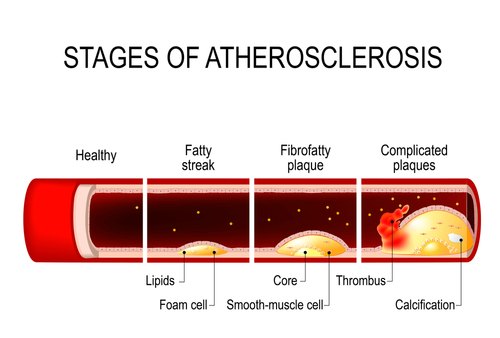
The production of Gla provides an extremely important role in preventing Vascular Mineralization (i.e arterial calcification).
Among the proteins involved in Vascular Calcium metabolism, there is one protein called the Matrix Gla protein (MGP) that inhibits arterial calcification.
Mouse studies where Vitamin K and MGP deficiency were invoked, the mice perished due to spontaneous calcification of arteries and cartilage.
Furthermore the drug industry market drugs to lower the viscosity of the blood (blood thinners) including Coumadin and Warfarin which we know from the Rotterdam study are antagonistic toward the functioning of Vitamin K (in fact they inhibit the liver enzymes responsible for VitK recycling as shown in diagram 2).
Another mouse study demonstrated the progression of arterial calcification when they were fed Warfarin.
Vitamin K proteins are not just restricted to blood plasma but have been found in snake venom to maintain appropriate viscosity.
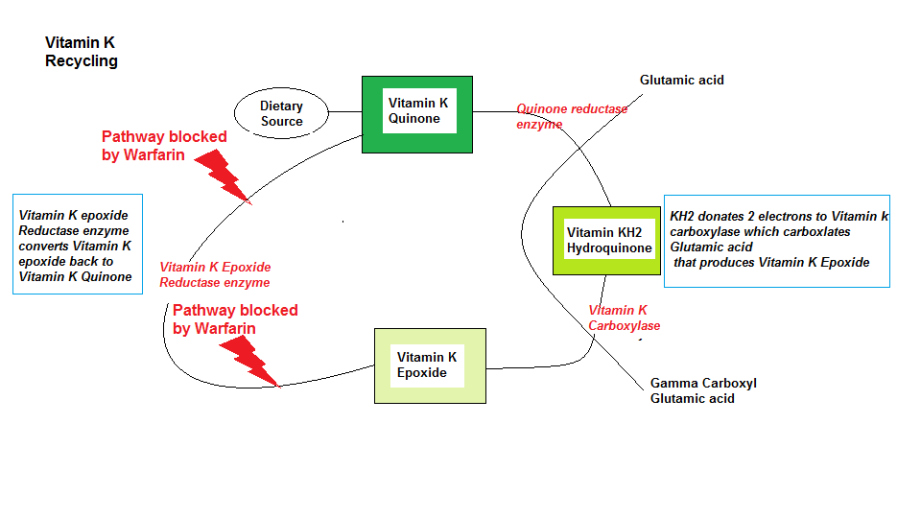
Vitamin K Recycling
As shown in Diagram 2 the Vitamin K recycling pathway within the liver is an efficient process to maintain this vital vitamin to be available for blood coagulation.
However, by taking the Blood thinner prescription drug Warfarin (Coumadin) they can block the recycling process in 2 places, thus inhibiting the natural blood coagulation process.
Conventional medicine insist that you avoid all dietary forms of Vitamin K since it interrupts their poison effectiveness
“So who’s going to tell our bacteria to stop producing K2 ?..oh yes antibiotics.”
Diagram 2: VitK Cycle (Vitamin K recycling)
Who’s Driving the Bus…Disease or Health Care?

I know I used this question before in the articles on Cancer, but it is a recurring question and will always be that way until conventional health care practices wake up which we all know will..’Not be in my lifetime’, that’s why we have the great men of true health science of today like Dr John B, Dr Joel Wallach, Dr Nicholas Gonzalez, Dr William Wolcott. Many more brilliant medical scientists that have come before, and some that have ‘felt the whip’ of conventional medical tyranny like the great Dr Max Gerson who fled the tyranny of Germany and into the hands of the ‘Medical Mafia’ in the US.
In the words of another great MD, Michael Gershon ‘ Discoveries are thus made and claimed that are really rediscoveries-not new advances at all, but history lessons’.
From the previous paragraph, dealing with soft tissue and arterial calcification, it would appear that these issues can be a real threat toward heart failure as opposed to the erroneous association of Cholesterol and Atherosclerosis.
Allopathic physicians never measure Vitamin K status, and even if they did they would measure the serum level which has no relevance toward clinical benefit, since the key is the tissue level of Active Carboxylated MGP which clears the calcium debris within the arteries.
Indeed it is the low levels of Uncarboxylated MGP that would be indicative of more widespread calcium deposits.
Furthermore, it is proposed that VitK may have a protective effect on the Kidney, where low levels of MGP also found in the kidney could also have a bearing on potential renal failure and its associative effect on the Bowman’s Capsule (the first stage of blood filtration in the kidney) and the Proximal Tubule (responsible for PH regulation of the filtrate within the kidney).
Finally, the association of bone integrity and active MGP alludes most physicians understanding of true health diagnosis, since it is easier just to prescribe a course of Fosamax or Boniva ( 2 drugs that inhibit osteoclastmediated bone resorption, so new bone is constantly built on old bone; now wonder people have brittle bones) rather than enquire your calcium, Vitamin D and K status.

The Rotterdam Study
There was a very famous study that began in 1990 in Rotterdam that studied some 8000 55 year olds that all lived in the Ommoord district of Rotterdam in terms of their Cardiovascular and Neurological health, and to discover why this elderly section of the population were living with disease and to discover the causes of their disease.
The study is ongoing (in 2014 it was), focusing on a variety of diseases like Coronary Heart disease, Heart Failure, Stroke, Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, Depression, Anxiety, Macular Degeneration, Glaucoma, Diabetes, and Osteoporosis.
The study also included nutrient deficiency and prescription drugs levels and their physiological synergism and antagonism respectively.
ViTK was studied extensively and its interrelationship with drugs such as Warfarin and Coumadin.
Investigatory areas included High body mass and kidney dysfunction and uncovered a correlation toward nerve dysfunction.
Changes in Carotid Plaque Components (Arterial Plaquing) and Intraplaque Hemorrhage (IPH), concluding that a high incidence of IPH was associated with the use of Antihypertensive drugs (Diuretics, Calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, Vasodilators, AND renin inhibitors).
Calcification, Dietary Acid load, Trabecular bone integrity (inner bone core ) and Mineral Density, concluding that a high protein intake versus vegetable sources showed negative consequences, and individuals with a high intake of dietary fibre and protein might be detrimental to bone integrity (although today this correlation toward high protein and bone integrity is questionable).

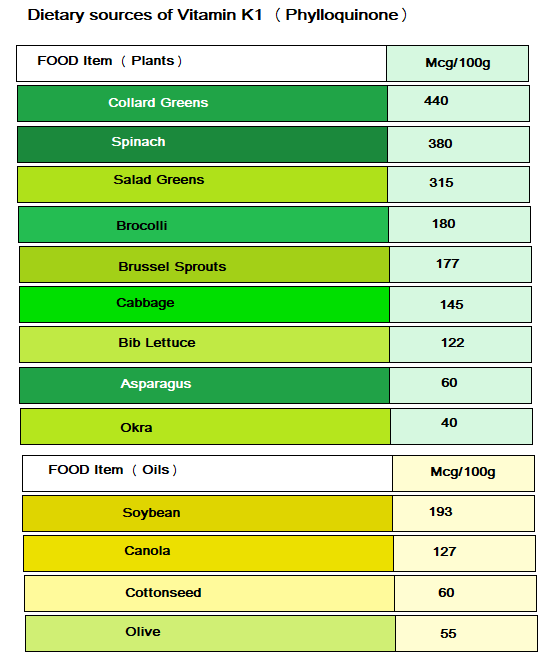
Dietary Sources of Vitamin K1(Phylloquinone)
The main dietary sources of VitK1 is plant food, although it can be found in small amounts in dairy, meats and eggs.
In the list below I have just included the foods that have the most amount of VitK1 since we only absorb 10% of this form of Vitamin.
Amounts that are < 100 mcg /100g, the values are almost insignificant, although having said that, a variety of foods could amount to the RDA which I have changed to 90 mcg (0.2mmol/day).
Table 1: Dietary sources of Vitamin K1 (Phylloquinone)
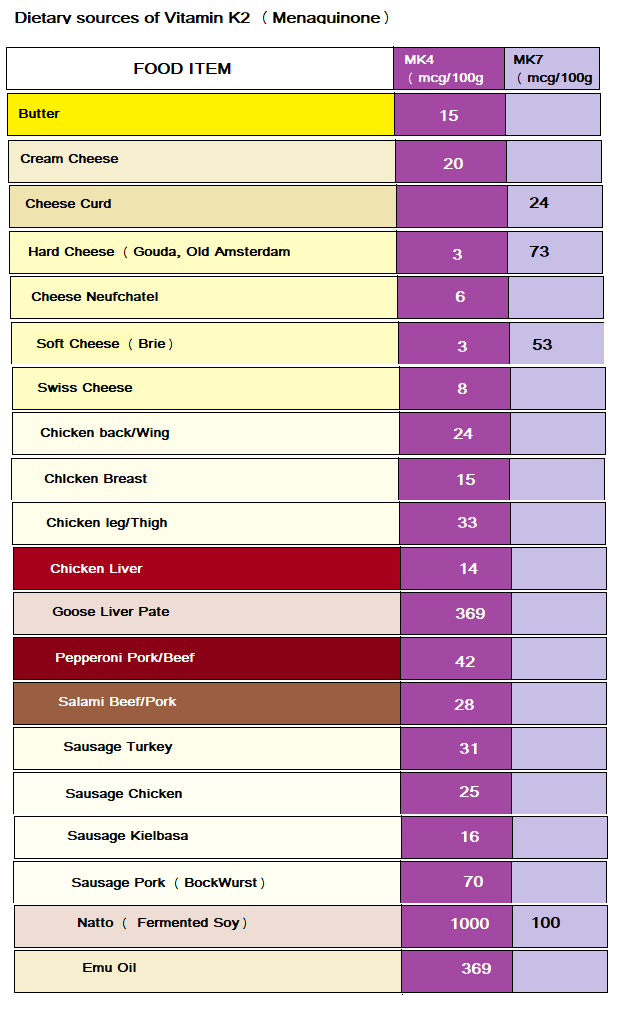
Dietary Sources of Vitamin K2 (Menaquinone)
This form of VitK2 is produced by Bacteria via two essential metabolic pathways called the Shikimate pathway which only our bacteria have access to ( The pathway used to produce 3 aromatic amino acids Phenylalanine, Tyrosine and Tryptophan which are essential to the host).
The second pathway is the Mevalonate pathway which is also known as the Isoprenoid or HMG-CoA Reductase pathway..yes you remember the same pathway that is blocked by Statin drugs in an attempt to cripple the liver’s ability to produce cholesterol.
Bacteria use this pathway to produce Isoprenoids like Cholesterol, Heme, Vitamin K and CoQ10.
These Isoprenoids are actually known as Terpenoids which provide the scent to Eucalyptus, and attribute the flavors of Cinnamon, Cloves and Ginger and whats makes a Tomato red.
Depending on the Terpenoid structure describes the number after the various forms i.e Mkn. The MK4 form is generally produced by humans and other mammals, MK7 is produced by bacteria. MK8,9,10 are found in small amounts in dairy foods, and other vitamer forms such as MK11 and 13 which are just trace amounts from Bacteria.
As we stated earlier VitK2 is synthesized by bacteria which generally include MK10 and MK11 by Bacteroides, MK8 by Enterobacter, MK7 by Veillonella, MK6 by Eubacterium lentum, and MK10-13 Bacteroides.
However, in 1964 it was discovered that E.Coli and Aerobacter Aerogenes synthesize K2 (MK8). Mycobacterium tuberculosi was also found to synthesize K2 by Almquist and Klose in 1939.
Apart from bacteria providing K2 for our benefit they actually produce it to derive energy themselves.
However, the various forms of K2 Menaquinone (MK) are found in foods as well as shown in Table 2.
A cautionary note here is required, which concerns the existence of an MK3 which is a man made synthetic and should be avoided.
Also ‘Vitamin K3 exists called Menadione which also should be avoided (K4 menadiol was a drug called Synkavite but that was withdrawn and K5 which should also be avoided).
Some of the poisonous oils contain K Vitamer (Dihydrophylloquinone) but since you are avoiding these damaged oils you will avoid this substance, which, incidentally interferes which natural vitamin K activity (you need to keep a watchful eye on these manufacturers).
Table 2: Dietary Sources of Vitamin K2 (Menaquinone)
Conversion of K2 to K1
In 1994 two scientists Thijssen & Driiij-Reijnders studied Vitamin K1 supplementation in a VitK free diet of a rat and they found that KI had accumulated with the higher levels in the Liver, Heart, Bone and Sternum, while lower levels were found the Brain.
In the K1 free rats there were found high levels of K1 in the Heart, Pancreas, Bone and Sternum (I suppose that prior to feeding the rat with a VitK1 free diet it had consumed some food that contained K1 for it to have accumulated and recycled).
In addition MK4 K2 was found in all tissues with low levels in the Plasma and Liver but much higher levels in the Pancreas, Salivary Gland and Sternum.
MK4 K2 levels in the brain were higher than K1 in the Brain, Pancreas,Salivary Gland and Sternum.
In the Liver were found MK6-9 that were accumulated in the Mitochondria.
The results concluded that there was a selective distribution of both K1 and MK4 K2 and that some K1 was converted to K2.
In 1964 Martius and Leuzinger confirmed that Phylloquinone (K1) could be converted to Menaquinone (K2) by Bacteria species Bacteroides Melaninogenicus. However, a K1 dietary source (without supplementation) is poorly absorbed and the liver will hold on to any K1 that is absorbed for coagulation purposes as a priority versus K1-K2 conversion.
Subsequent studies done in 1998, 2006 and 2013 confirmed that this conversion takes place and that an intermediary step is involved that of Menadione (VitK3.the natural substance not the poisonous one) which is made in the intestine from K1.
I am not sure why they had to spend time and money confirming what they found in 1994, when in fact, they could have studied the amount of K2 that is produced by our bacteria, and then confirm how much K1 is absorbed, analyze tissue samples to see what goes where and how much, and then ascertain the biological decisions that are made by the central distribution channel the liver.
Having said that, the discovery of an intermediary step using Vitamin K3 for the K1-K2 conversion was interesting.
Please do not misunderstand me, the work these scientists do is remarkable and time consuming, but if we are to advance our knowledge we need to ‘mix it up’ a little in terms of scientific study.
There is still much we don’t know..If our bacteria can convert KI-K2, do they actually perform this function, and under what circumstances do they perform this function, and is there any benefit to the host.
The host can also perform this operation and if the host is deficient in dietary K2 then in theory the host should get enough produced by the bacteria.
I can only hypotheisize that the Liver’s decision to perform the KI-K2 conversion is based on the amount that the bacteria produces and the hosts dietary intake, but K1 will always take priority since it is involved in Blood clotting versus K2 that directs calcium into the correct locations ( Survival over bone loss).
Furthermore is absorption rate is so poor for KI there would never be enough K1 for this conversion to occur within the host. This begs a follow on question, is the Liver capable of converting K2-K1 ?.
I suspect that in time we need to update our knowledge on this crucial Vitamin.

Then I had shown, in the same place, what the structure of the nerves and muscles of the human body would have to be in order for the animal spirits in the body to have the power to move its members, as one sees when heads, soon after they have been cut off, still move and bite the ground even though they are no longer alive; what changes must be made in the brain to cause waking, sleep and dreams; how light, sounds, odours, tastes, warmth and all the other qualities of external objects can impress different ideas on it through the senses; how hunger, thirst, and the other internal passions can also send their ideas there; what part of the brain should be taken as “the common sense”, where these ideas are received; what should be taken as the memory, which stores the ideas, and as the imagination, which can vary them in different ways and compose new ones and, by the same means, distribute the animal spirits to the muscles, cause the limbs of the body to move in as many different ways as our own bodies can move without the will directing them, depending on the objects that are present to the senses and the internal passions in the body. This will not seem strange to those who know how many different automata or moving machines can be devised by human ingenuity, by using only very few pieces in comparison with the larger number of bones, muscles, nerves, arteries, veins and all the other parts in the body of every animal. They will think of this body like a machine which, having been made by the hand of God, is incomparably better structured than any machine that could be invented by human beings, and contains many more admirable movements.
-René Descartes (1596 – 1650)
Check out the Previous Article in this series:
https://www.extremehealthacademy.com/90-essential-nutrients-part-1-overview/
https://www.extremehealthacademy.com/90-essential-nutrients-part-2-b-vitamins-1-6/
https://www.extremehealthacademy.com/90-essential-nutrients-part-3-b-vitamins-7-12/
https://www.extremehealthacademy.com/90-essential-nutrients-part-4-vitamins-acde/
https://www.extremehealthacademy.com/90-essential-nutrients-vitamin-d/
https://www.extremehealthacademy.com/essential-nutrients-vitamin-e/
References/Acknowledgments:
- Youtube interview with Dr Surgis from Maastricht University on Vitamin KI/K2
- MGP, Vitamin K, Terpenoids, Bowman’s Capsule/Proximal tubule Wikipedia
- Matrix Gla Protein, the calcification inhibitor in need of Vitamin K J.Schurgers, E.Cronenberg, C.Vermeer NIH 2008
- Vitamin K Coagulation slides jsmu.edu.pk/lectures website
- Matrix Gla Protein (MGP) not only inhibits calcification in large arteries but also may be renoprotective: Connecting the dots M.Epstein 2016 EbioMedicine Website
- Modern Nutrition in health and disease M.Shils, M.Shike, C.Ross, B.Cabellero, R.Cousins
- Vitamin K2 Dr Cannell 2013 Vitamin D Council
- Descarte quote TODAYINSCI website
- The second brain Book Michael Gershon MD
Author: Eric Malouin